Table of Contents
Ginger, one of the most pungent yet flavorful culinary ingredients, can be found practically everywhere in the world. It is botanically categorized as a rhizome, which is a type of underground stem. Many DIY gardening enthusiasts often wonder if ginger grows back every year, and the answer to this question is yes. Grow ginger UK is a perennial plant that keeps coming back year after year.
Ginger is a highly versatile tool in the hands of a chef as it can be the star ingredient of sweet dishes like gingerbread cookies but also works equally effectively as an aromatic ingredient in soups and broths.
Can Ginger Grow Back Every Year?
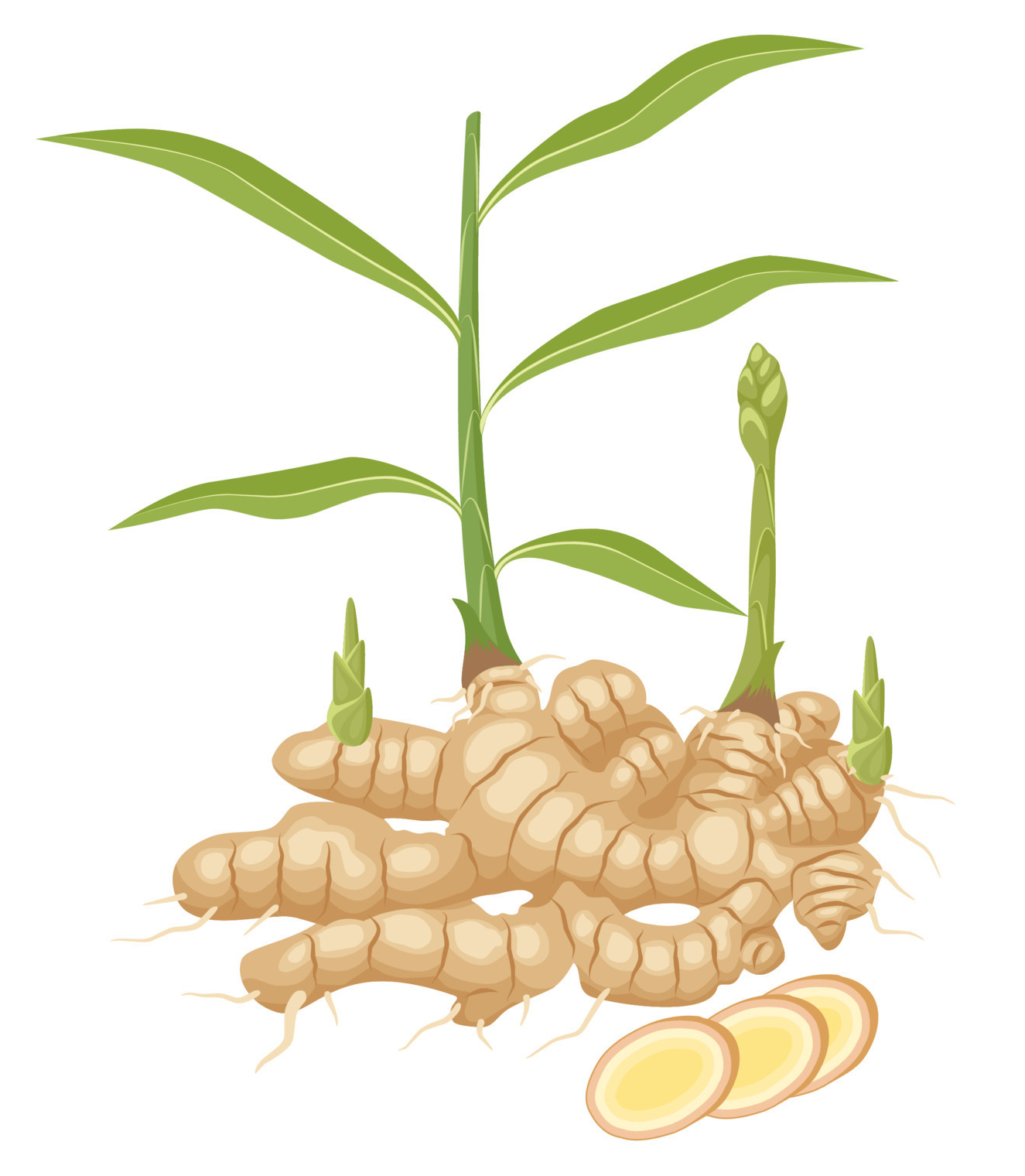
Yes. Ginger can grow back every year owing to its perennial nature. The herbaceous perennial was first discovered in Southeast Asian countries; therefore, the plant thrives in regions that are humid and have a warm climate. The ideal temperature for ginger to grow ranges between 60℉ and 90℉ grows best when planted outdoors.
How to Grow Ginger?
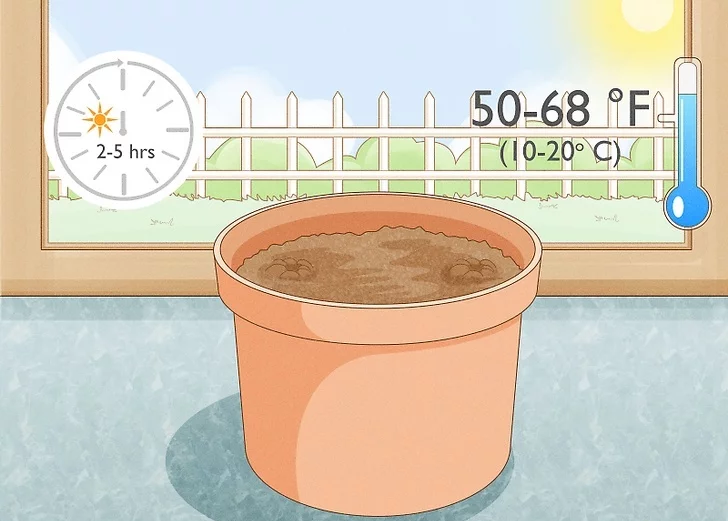
1. Start by selecting a well-drained acidic potting soil. Select a rich, loamy soil for the best growth. Make sure that the soil is moist but not soggy because the roots need moisture to grow. However, extremely wet soil can cause the roots of the plant to rot.

2. For those growing ginger in pots, sow your ginger bulbs in early spring if you are living in a cold region. However, if the climate of your place is warm and humid, you can start the process at any point of time in the year.
3. Cut off the fingers. The size of each finger must be 2-4 inches in length, and it must have at least one bud. Lightly add some soil over the rhizomes as they grow and increase in number.
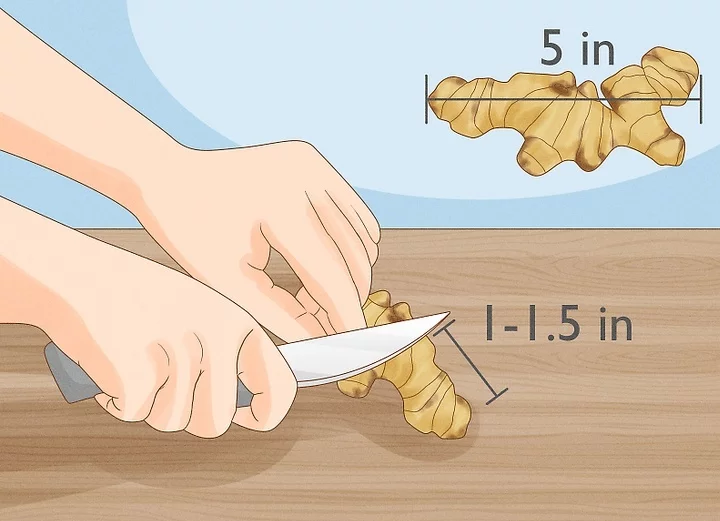
4. Now plant these pieces not more than 1 inch deep into the prepared soil. If you are growing these root plants in the ground, make sure that they are at least 12 inches apart.

5. Water the plant generously, and leaves will start emerging after one week. Once the growth starts, the ginger will reach a height of 4 feet, and the roots will appear above the ground.
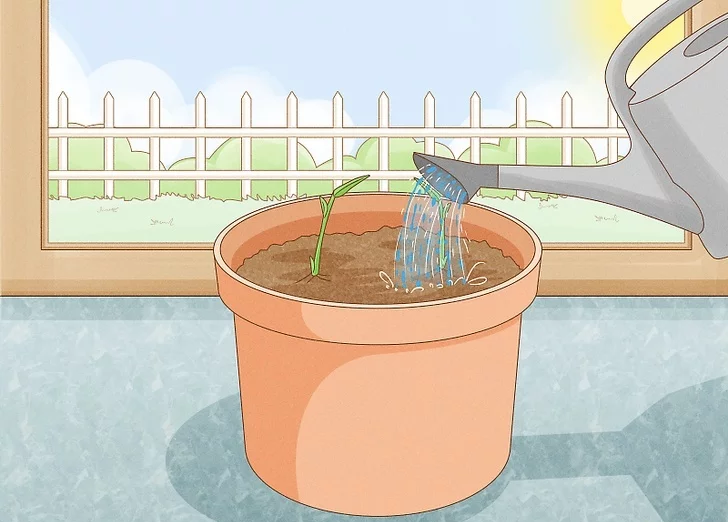

Harvesting Ginger
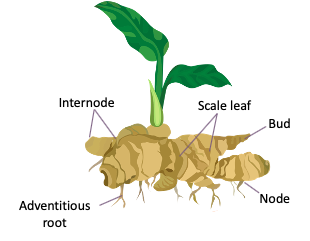
- Ginger can be harvested in 8-10 months, i.e., once the leaves start turning yellow. Dig up the rhizomes, remove what you need, and replant them for the next season.
- Select those portions of the harvested rhizomes that have buds or eyes for replanting. Make sure that the part selected for cutting into smaller parts has at least one healthy bud.
- Allow these small sections to air dry till a protective layer is formed around them,
- Plant the prepared rhizome sections 2 to 4 inches deep into the soil with buds facing upward.
- Care for the plant continuously by exposing the rhizome to the required warmth and humidity and ensuring a proper supply of nutrition.
Do’s and Don’ts for Growing Ginger

There are various external conditions that must be monitored to ensure the healthy growth of a plant.
- Correct Lighting Conditions: A ginger plant grows best in bright but indirect light or when placed under the morning Sun for a few hours. The plant will need some protection from the bright afternoon sun so that the leaves do not get scorched.
- Maintaining The Right Temperature: Ginger grows well as an outdoor container plant. The temperature should be somewhere between 60℉ and 90℉. However, shift the plant inside if the temperature goes below 55℉.
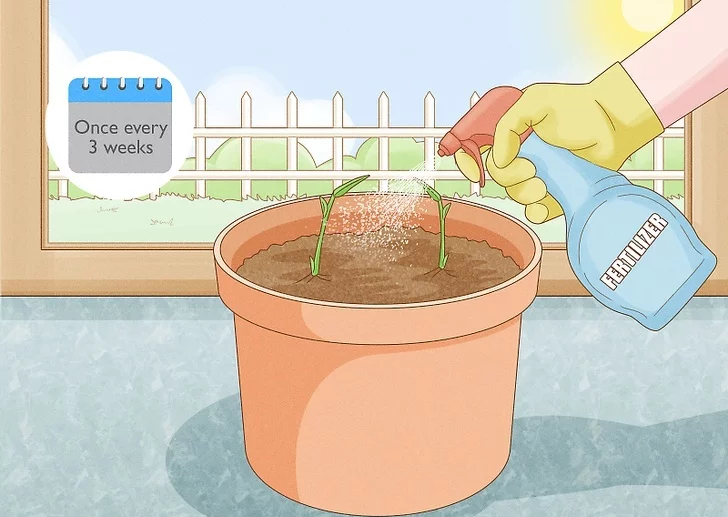
- Selecting Fertilizer: Nourishing the soil with the right fertilizer is a must. To do so, mix a slow-release fertilizer into the gardening soil. You can even opt for a liquid fertilizer such as a fish emulsion or kelp that is supposed to be applied once in 3-4 weeks.
- Soil and Water Ratio: Ginger grows best in soil that has a pH level that ranges between 6 and 6.5. If you are growing ginger in the ground, ensuring proper drainage is a must, and to help retain moisture in the soil, add plenty of compost. For those who wish to grow ginger in a pot, invest in a high-quality potting mix.
Conclusion
Perennial plants are those that survive for more than 2 years, and ginger fits this description perfectly. When you harvest ginger, you do not have to start from scratch, as you can replant a portion of the rhizome. With proper care, it will sprout new shoots and produce fresh ginger. Its ability to grow repeatedly, when provided with the right conditions, makes it a unique addition to any kitchen garden.
If you have green fingers and want to add something beneficial to your kitchen garden, try growing ginger and share your experience with us.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Pests Can Attack the Ginger Plant?
Aphids, ants, mealy bugs, spider mites, cutworms, slugs, and snails are some of the most common pests that attack a healthy ginger plant.
After How Much Time Does the Ginger Plant Gain Maturity?
A ginger plant will attain full maturity after 210-240 days or 8-10 months after planting. The leaves start turning yellow and wither away. Harvesting of ginger for vegetable purposes, on the other hand, starts after 180 days.
Is Ginger a Seasonal Plant?
Ginger is a perennial plant that thrives in tropical regions. It does not follow the typical seasonal growth patterns but grows best in warm and humid conditions.





